Drupal is a secure CMS used by almost 3% of websites worldwide. Since its creation in 2000, the web application has seen limited Drupal security vulnerabilities when compared with other popular CMS platforms. For this reason, organizations around the world have decided to rely on Drupal, and its ability to provide the site foundation they need to remain secure.
However, Drupal is not flawless. It has its own unique Drupal security problems. There have been Drupal security vulnerabilities associated with the CMS — some of which have been severe for site owners. These vulnerabilities have often attacked outdated or unmaintained areas of Drupal Code. In many cases, these attacks would have been prevented if site owners had adhered to Drupal security best practices.
Starting with a brief history of Drupal security, this guide looks at the biggest Drupal security problems, what exploits are most commonly attributable to Drupal, how you can protect your site with Drupal security features, and who can help you to protect your Drupal site.
We’ll cover:
- What Drupal security problems are most common with this CMS.
- How to prevent those vulnerabilities from causing damage with Drupal security features.
- Who is responsible for specific areas of Drupal security and site protection.
- Where you can go for more information and guidance.
Is Drupal Secure?
Drupal is often praised as being highly secure. At its foundation lies a stable source code with limited vulnerabilities and a sizeable support community. According to research by Imperva, Drupal is more secure than most other popular web applications, including WordPress, Magento, and Joomla. In 2018, it was found that only 11% of 2018’s identified vulnerabilities came from Drupal, far below the number attributed to WordPress.

Yet there are a number of Drupal security problems and those vulnerabilities exist in varying form. CVE research identified a total of 323 recorded Drupal Vulnerabilities since 2002. Of these vulnerabilities, 42% were cross-site scripting (XSS) issues and 14% were code execution vulnerabilities. Other vulnerabilities that were statistically apparent included SQL injection and bypasses.

Drupal Security
In 2018, Drupal was the web application target of choice for many attackers. Despite having fewer vulnerabilities than counterparts, the vulnerabilities it did have were relatively easy to exploit.
Two of the worst attacks of 2018 came in the form of Drupalgeddon2 and Drupalgeddon3 (also known as CVE-2018-7600 and CVE-2018-7602). These vulnerabilities were exploited by remote attackers injecting malicious code. This code then allowed them to mine data, scan internal networks, insert trojans, and more.
Druaplgeddon2
The first of these, Drupalgeddon2, struck on March 23. It worked through a code injection vulnerability associated with Drupal’s forms. A carryover from Drupal 6, the form rendering process vastly improved the way form markup was done, but ultimately led to an exploitable entry point in the email field. 94% of attackers used the vulnerability to scan sites for other vulnerabilities, while 2% attempted Crypto mining.
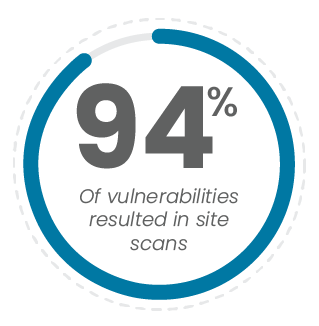
Once discovered, the introduction of a new WAF rule by Nexcess meant that this exploitation was quickly stopped for our clients.
Druaplgeddon3
Drupalgeddon3 then struck in late April. Again attacking the form API, this flaw resided in the destination parameter. Again, this was a code execution vulnerability that led to site takeovers. While Drupalgeddon3 was just as severe as Drupalgeddon2, it actually resulted in fewer recorded attacks due to requiring the attacker to be authenticated on the attacked host. A properly configured WAF from a hosting provider like Nexcess would have been able to prevent this attack from taking place.
Drupal Security
Several sources have predicted that injection vulnerabilities will continue to grow in number, largely because it’s possible to make money with these attacks. For Drupal site owners, this means that it’s important they secure their sites and ensure they have an up-to-date WAF. Learn more about the Nexcess WAF.
Another exploit that will be taken advantage of is outdated PHP versions. 2019 has seen PHP 7.0 and 7.1 reach end of life, meaning they will no longer receive security updates. Drupal is developed in PHP, so all site owners should make it a priority to update their PHP version. PHP versions can quickly be changed by Nexcess cloud clients in the Client Portal. We recommend testing any changes on a dev site before sending to a production site.
Is Drupal Secure Long Term?
As complex software, Drupal occasionally suffers from bugs that cause software vulnerabilities. This is true of all content management systems. The way projects handle vulnerabilities when they are discovered is just as important as their commitment to minimizing vulnerabilities in the first place. Vulnerabilities should be fixed quickly and a patch released so that users can protect themselves. Thanks in large part to the security team, Drupal has an excellent track record. The developers are responsive to vulnerability reports and they release patches quickly.
In addition to the Security Team, Drupal has a couple of other advantages that businesses should know about when choosing a CMS: it is open source and major versions of Drupal receive security updates for many years.
Because Drupal is open source, its code is open to scrutiny by users, developers, and the wider community. It is based on an open source web framework (Symfony) that is open to the same scrutiny. Unlike proprietary content management systems, the Drupal project has no incentive to keep vulnerabilities secret and every incentive to fix them quickly.
The Drupal Versions
Drupal 8, the most recent major version, was released in November 2015 and will reach the end of its life in November 2021. Drupal 7, which was released in 2011, will also be retired in 2021. With a 10- and 6-year lifespan, Drupal 7 and 8 have received security updates for longer than most competing content management systems, keeping Drupal sites secure without requiring disruptive upgrades.
In the future, the long lifecycle of Drupal versions will be less of an issue because it will be much easier to upgrade to Drupal 9 from Drupal 8 than previous major versions. However, there is likely to be commercial support for older versions, as there still is for Drupal 6, which was first released in 2008.
How To Keep Drupal Secure
Keep Modules and Core Up to Date
Keeping modules up to date is as important as keeping your site up to date. Community contributions are released constantly, with many addressing important security risks. The further you fall behind with Drupal updates, the more vulnerabilities your site will be exposed to and the more likely you are to have a security lapse.
If your site is not updated, you will be reminded of this when you go to create new content. This warning message should not be ignored – especially considering that it’s a relatively quick fix.
To find and install new updates to your Drupal site, simply open Reports, then click Available Updates and Check Manually. Once you’ve found security updates, you can click download and install them by clicking the Install New Module Or Theme button.
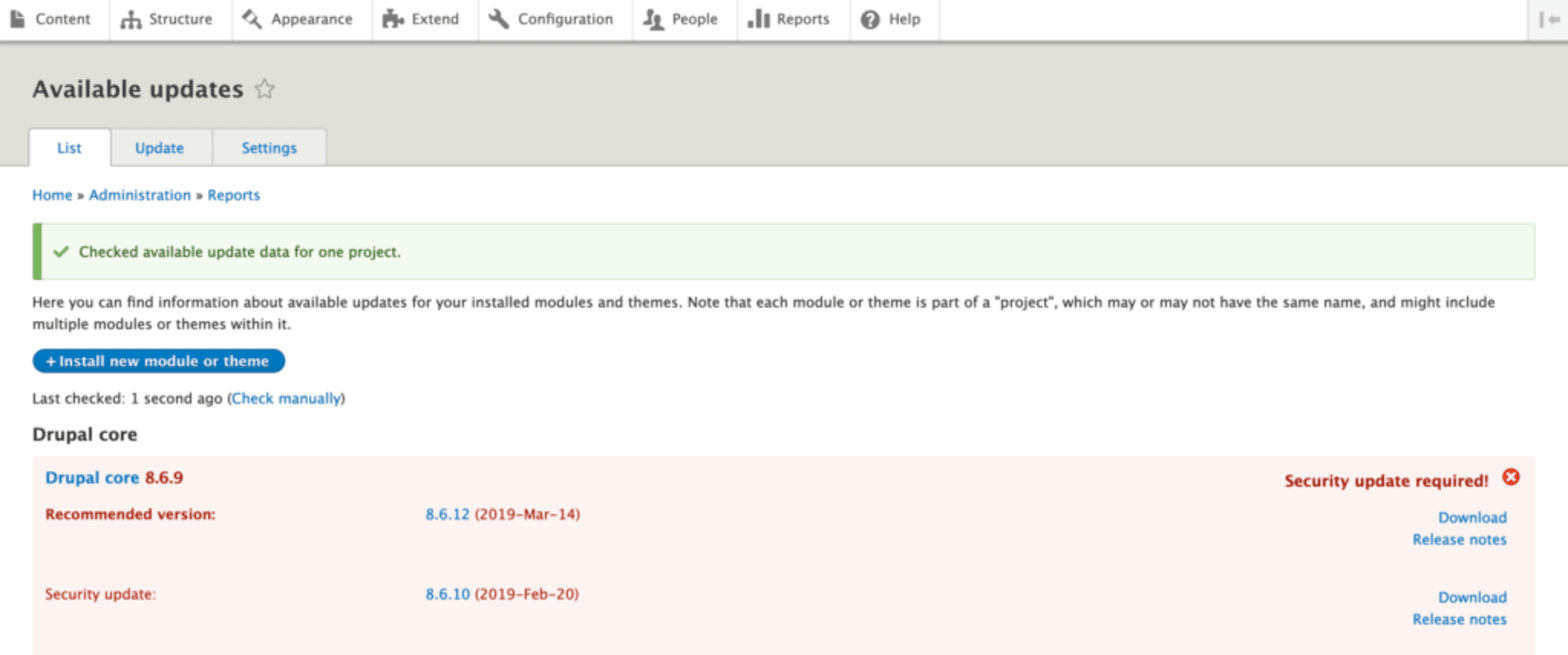
If you’re starting a new site, it’s always a good idea to start with the latest version of Drupal. You can find the latest version of Drupal on their site: drupal.org.
Implement Better Passwords
As a PCI compliant hosting provider, this is something we come across frequently. Passwords are important and should always be chosen carefully. We’ve all heard the joke about the user whose password is “password”. But if we take a look at the top 25 passwords used globally, we begin to realize that it’s more than just a joke.
Implementing a better password may just mean using a password generator. These allow you to define parameters for what password you need and then generate it. If you’re afraid of not remembering your password, a password storage tool such a LastPass can help.
Finally, even with a better password, you should still be implementing additional security measures. We always recommend 2FA.
Add Drupal Security Modules
The first security module you should be adding is one that enables 2FA. The Two-factor Authentication (TFA) module is perfect for this. Note that at the time of writing this module is in alpha for Drupal 8.
Other security modules that will help you to lock down your site include:
Login Security: Deny login access based on IP address and number of login attempts.
Automated Logout: Log users out after a user-defined timeout period.
Session Limit: Limit the number of simultaneous sessions per user.
SpamSpan Filter: Blocks bots from finding email addresses by obfuscating them.
Drupal Security Review: Runs tests for common security issues that include insecure file system permissions, admin permissions, failed login attempts, database errors, and more. This module is the best way to find out if a Drupal site is vulnerable to attack.
Security Kit: Extends Drupal’s built-in security features with extra security-hardening options such as content security policy (CSP) implementation, cross-site request forgery protection, and HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS).
Prevent Indexing of the Login Page
You access your Drupal admin panel by logging into your site. An attacker can do the same. A simple and effective way to prevent unauthorized logins to your site is to prevent indexing of the login page by search engines. This makes it harder for an attacker to find your login page. You can do this by entering the following line in your Robots.txt file under Paths.
Disallow: /user/login
Check Files Permissions
File permissions play an important role in Drupal security implementation. They allow you to see which people are able to read, write, and modify content on your website. If you open permissions up to too many people, it is easy for attackers to gain access to your site. Conversely, if they’re too strict, you can end up breaking parts of your site.
Drupal themselves talk about how to secure file permissions. As a general rule, it’s important to keep permission for core files and directories such as modules and index.php locked to admin users only.
Block Important File Access Entirely
Certain files are sensitive and shouldn’t be accessed by anyone other than the site’s primary administrator. This includes upgrade.php, cron.php, install.php, and authorize.php. To do this, you can add the following to your .htaccess file.
Order deny, allow deny from all Allow from 1[Insert Your IP]
Block Bad Bots
Bots, crawlers, and scrapers are a constant danger to sites. If they don’t do anything else, they can steal your bandwidth. In most cases, security extensions like SpamSpan Filter and Session Limit can help to ease the effects of bad bots. However, there are sometimes instances where it’s important to block bad bots not covered by these modules.
To block bad bots at the server level, you’ll need to limit the number of user-agent strings by adding the following to your .htaccess file.
RewriteEngine On RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} ^.*(agent1|Wget|Catall Spider).*$ [NC] RewriteRule .* - [F,L]
If you host your Drupal site with a secure hosting provider, always check to see what they are doing to protect your Drupal site from bad bots. Nexess ensure bad bot protection for clients across our entire network by limiting traffic from known offenders and employing continuous site monitoring to identify new ones.
Always Keep a Backup of Your Site
It’s recommended that you always have an up-to-date backup of your site. This does not mean just relying on your hosting provider’s backups. In some cases, corruption and vulnerability exploits can damage both their backup and the original. For this reason, it’s recommended to also store a backup of your site locally.
This can be done in a variety of ways. We recommend storing a backup of your MySQL databases and your Drupal file directory. With Nexcess it is possible to automate this process and download site backups through your control panel. We recommend making a full backup.
Install an SSL Certificate
An SSL certificate is a small file that digitally adds a cryptographic key to an organization’s domain. This allows for secure connections from a web server to a browser through https. SSL certificates are particularly important for login and checkout processes. By keeping the information being transferred secure, it prevents attackers and identity thieves from accessing that information.

For eCommerce sites, an SSL certificate can make a huge difference to revenue. 61% of shoppers will not purchase from an unsecured site and 98% will not proceed past an unsecured site warning.
If you’re unsure what SSL certificate is right for you site, we recommend looking at our SSL FAQ. Note that it’s important to install an SSL certificate for more than just security. In 2014, Google announced that the presence of https will influence site ranking in search results.
Purchase an SSL Certificate Now.
Who Can Help You With Drupal Security?
The Drupal security ecosystem relies on three groups to help identify issues, fix breaches, and maintain security for site owners. Each of these groups has a vital role to play and can help in unique ways, If you’re a Drupal site owner and run into a problem, these are the four main groups who can help.
Developers
Your developers are uniquely placed to identify and fix issues that may have been missed. They have firsthand experience navigating your Drupal site. Often, dedicated Drupal developers will contribute to a Drupal site on a daily basis, whether that’s one or multiple. This means that they are constantly collecting information about potential vulnerabilities. Moreover, a developer may be the most immediate source of help available.
Hosting Providers
Hosting providers are your second line of defence against vulnerabilities. Often, if you are hosting with a reliable provider, their infrastructure is optimized to try and protect you against vulnerabilities and security exploits. This often includes the implementation of a WAF (Web Application Firewall). A well secured WAF can mean a quick fix for dangerous vulnerabilities such as Drupalgeddon2 and Drupalgeddon3.
Project Maintainers
Project maintainers are on the frontlines of security, finding new problems every day and implementing solutions. There are more than 15,000 active project maintainers in the Drupal community and each one contributes their own areas of expertise, from plug-in modules to core. If you’re looking for a fix, or want to report on a vulnerability you’ve found, they are a good point of contact.
The Drupal Security Team
The Drupal security team are the core force behind protecting Drupal instances. Comprised of some of the world’s leading web security experts, the Drupal security team are always on call to assess and fix any issues that arise.
Drupal Security Advisories
Drupal themselves have a detailed list of security advisories. If you’re in charge of security for a Drupal site, it’s advisable that you check these relatively frequently. Each is marked depending on its security risk. If you see something that is highly critical, and your site meets the conditions, you should update your Drupal instance as soon as possible.
You can find the list of Drupal Advisories here.
If you’re unsure about whether you are affected, or would like help from the Nexcess team in employing a fix, you can contact support. They will help to resolve the vulnerability for you.
Conclusion
Drupal is one of the most secure web applications around. The Open Web Application Security Project maintains a list of the top-ten security vulnerabilities on the web. Drupal is engineered to mitigate the risk of each vulnerability on the list and many more. However, this doesn’t mean that you can sit back and do nothing. If you want your Drupal site to remain secure, it’s important to regularly update your site and follow security best practices as outlined above.
By following the best practices outlined in this guide, your site will remain safe and secure. However, it’s important to keep in mind that a “one size fits all” approach is not always the best way to proceed. You may find that by limiting permissions or editing defaults, your site will break.
For this reason, it’s highly recommended to first try all changes on a development site and then implement on production.
If you’re still unsure on something regarding Drupal security, why not speak to a Nexcess team member? We can walk you through how to keep you site secure and how our cloud hosting plans are engineered to maintain security.

